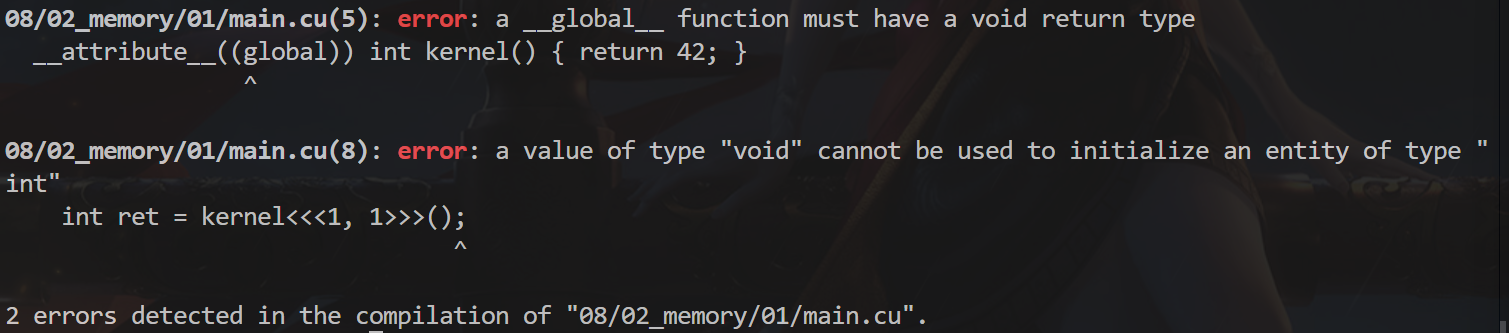
第二章:内存管理 怎样从核函数返回数据? 我们试着把 kernel 的返回类型声明为 int,试图从 GPU 返回数据到 CPU。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 #include <cuda_runtime.h> #include <cstdio> __global__ int kernel () { return 42 ; }int main () int ret = kernel<<<1 , 1 >>>(); cudaDeviceSynchronize (); printf ("%d\n" , ret); return 0 ; }
但发现这样做会在编译期出错,为什么?
刚刚说了 kernel 的调用是异步 的,返回的时候,并不会实际让 GPU 把核函数执行完毕,必须 cudaDeviceSynchronize() 等待它执行完毕(和线程的 join 很像)。
所以,不可能从 kernel 里通过返回值获取 GPU 数据,因为 kernel 返回时核函数并没有真正在 GPU 上执行。所以核函数返回类型必须是 void。
试图解决:通过指针传递 那你可能会想,既然不能返回,那作为指针传入局部变量的引用,不就好了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 #include <cuda_runtime.h> #include <cstdio> __global__ void kernel (int *pret) { *pret = 42 ; }int main () int ret = 0 ; kernel<<<1 , 1 >>>(&ret); cudaDeviceSynchronize (); printf ("%d\n" , ret); return 0 ; }
这样,在 cudaDeviceSynchronize() 以后,应该可以获取数据了吧?
结果令人失望,尽管给 kernel 传了指向 ret 的指针,但 ret 的值并没有被改写成功。
分析返回错误的代码 CUDA 的函数,如 cudaDeviceSynchronize()。
它们出错时,并不会直接终止程序,也不会抛出 C++ 的异常,而是返回一个错误代码,告诉你出的具体什么错误,这是出于通用性考虑。
这个错误代码的类型是 cudaError_t,其实就是个 enum 类型,相当于 int。
可以通过 cudaGetErrorName 获取该 enum 的具体名字。这里显示错误号为 700,具体名字是 cudaErrorIllegalAddress。意思是我们访问了非法的地址,和 CPU 上的 Segmentation Fault 差不多。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 #include <cuda_runtime.h> #include <cstdio> __global__ void kernel (int *pret) { *pret = 42 ; }int main () int ret = 0 ; kernel<<<1 , 1 >>>(&ret); cudaError_t err = cudaDeviceSynchronize (); printf ("error code: %d\n" , err); printf ("error name: %s\n" , cudaGetErrorName (err)); printf ("%d\n" , ret); return 0 ; }
helper_cuda.h工具 其实 CUDA toolkit 安装时,会默认附带一系列案例代码,这些案例中提供了一些非常有用的头文件和工具类,比如这个文件:
1 /opt/cuda/samples/common/inc/helper_cuda.h
把它和 helper_string.h 一起拷到头文件目录里,然后改一下 CMakeLists.txt 让它包含这个头文件目录。
它定义了 checkCudaErrors 这个宏,使用时只需:
1 checkCudaErrors(cudaDeviceSynchronize())
即可自动帮你检查错误代码并打印在终端,然后退出。还会报告出错所在的行号,函数名等,很方便。
示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 #include <cuda_runtime.h> #include <cstdio> #include "helper_cuda.h" __global__ void kernel (int *pret) { *pret = 42 ; }int main () int ret = 0 ; kernel<<<1 , 1 >>>(&ret); checkCudaErrors (cudaDeviceSynchronize ()); return 0 ; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 cmake_minimum_required (VERSION 3.10 )set (CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 17 )set (CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE Release)project (hellocuda LANGUAGES CXX CUDA)add_executable (main main.cu)target_include_directories (main PUBLIC ../../include )
在堆上分配试试呢? 你可能会想,难道是因为我的 ret 创建在栈上,所以 GPU 不能访问,才出错的?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 #include <cuda_runtime.h> #include <cstdio> #include "helper_cuda.h" __global__ void kernel (int *pret) { *pret = 42 ; }int main () int *pret = (int *)malloc (sizeof (int )); kernel<<<1 , 1 >>>(pret); checkCudaErrors (cudaDeviceSynchronize ()); free (pret); return 0 ; }
试图用 malloc 在堆上分配一个 int 来给 GPU 访问,结果还是失败了。
原因:GPU 使用独立的显存,不能访问 CPU 内存 原来,GPU 和 CPU 各自使用着独立的内存。CPU 的内存称为主机内存(host)。GPU 使用的内存称为设备内存(device),它是显卡上板载的,速度更快,又称显存。
而不论栈还是 malloc 分配的都是 CPU 上的内存,所以自然是无法被 GPU 访问到。
因此可以用用 cudaMalloc 分配 GPU 上的显存,这样就不出错了,结束时 cudaFree 释放。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 #include <cuda_runtime.h> #include <cstdio> #include "helper_cuda.h" __global__ void kernel (int *pret) { *pret = 42 ; }int main () int *pret; checkCudaErrors (cudaMalloc (&pret, sizeof (int ))); kernel<<<1 , 1 >>>(pret); checkCudaErrors (cudaDeviceSynchronize ()); cudaFree (pret); return 0 ; }
注意到 cudaMalloc 的返回值已经用来表示错误代码,所以返回指针只能通过 &pret 二级指针。
反之亦然,CPU 也不能访问 GPU 内存地址 你可能已经迫不及待想通过 *pret 访问其返回值了。但是不行,因为 GPU 访问不了 CPU 的内存地址,同理,CPU 也访问不了 GPU 的内存地址。一访问 CPU 就奔溃了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 #include <cuda_runtime.h> #include <cstdio> #include "helper_cuda.h" __global__ void kernel (int *pret) { *pret = 42 ; }int main () int *pret; checkCudaErrors (cudaMalloc (&pret, sizeof (int ))); kernel<<<1 , 1 >>>(pret); checkCudaErrors (cudaDeviceSynchronize ()); printf ("result: %d\n" , *pret); cudaFree (pret); return 0 ; }
跨 GPU/CPU 地址空间拷贝数据 因此可以用 cudaMemcpy,它能够在 GPU 和 CPU 内存之间拷贝数据。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 #include <cuda_runtime.h> #include <cstdio> #include "helper_cuda.h" __global__ void kernel (int *pret) { *pret = 42 ; }int main () int *pret; checkCudaErrors (cudaMalloc (&pret, sizeof (int ))); kernel<<<1 , 1 >>>(pret); checkCudaErrors (cudaDeviceSynchronize ()); int ret; checkCudaErrors (cudaMemcpy (&ret, pret, sizeof (int ), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost)); printf ("result: %d\n" , ret); cudaFree (pret); return 0 ; }
这里我们希望把 GPU 上的内存数据拷贝到 CPU 内存上,也就是从设备内存(device)到主机内存(host),因此第四个参数指定为 cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost。
同理,还有 cudaMemcpyHostToDevice 和 cudaMemcpyDeviceToDevice。
cudaMemcpy 会自动同步! 注意:cudaMemcpy 会自动进行同步操作,即和 cudaDeviceSynchronize() 等价!因此前面的 cudaDeviceSynchronize() 实际上可以删掉了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 #include <cuda_runtime.h> #include <cstdio> #include "helper_cuda.h" __global__ void kernel (int *pret) { *pret = 42 ; }int main () int *pret; checkCudaErrors (cudaMalloc (&pret, sizeof (int ))); kernel<<<1 , 1 >>>(pret); int ret; checkCudaErrors (cudaMemcpy (&ret, pret, sizeof (int ), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost)); printf ("result: %d\n" , ret); cudaFree (pret); return 0 ; }
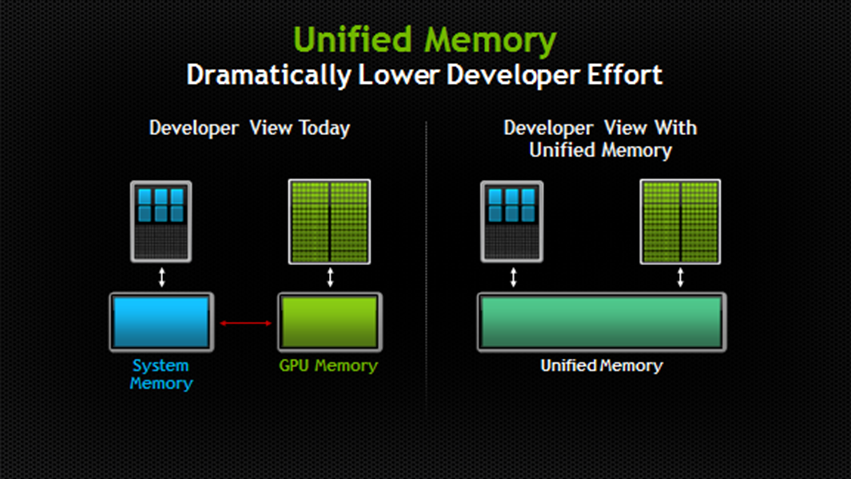
统一内存地址技术 (Unified Memory) 还有一种在比较新的显卡上支持的特性,那就是统一内存(managed),只需把 cudaMalloc 换成 cudaMallocManaged 即可,释放时也是通过 cudaFree。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 #include <cuda_runtime.h> #include <cstdio> #include "helper_cuda.h" __global__ void kernel (int *pret) { *pret = 42 ; }int main () int *pret; checkCudaErrors (cudaMallocManaged (&pret, sizeof (int ))); kernel<<<1 , 1 >>>(pret); checkCudaErrors (cudaDeviceSynchronize ()); printf ("result: %d\n" , *pret); cudaFree (pret); return 0 ; }
这样分配出来的地址,不论在 CPU 还是 GPU 上都是一模一样的,都可以访问。而且拷贝也会自动按需进行(当从 CPU 访问时),无需手动调用 cudaMemcpy,大大方便了编程人员,特别是含有指针的一些数据结构。
注意区分
如果我没记错的话,统一内存是从 Pascal 架构开始支持的,也就是 GTX9 开头及以上。
虽然方便,但并非完全没有开销,有条件的话还是尽量用分离的设备内存和主机内存吧。