第六章:thrust库
使用 CUDA 官方提供的 thrust::universal_vector
虽然自己实现 CudaAllocator 很有趣,也帮助我们理解了底层原理。但是既然 CUDA 官方已经提供了 thrust 库,那就用他们的好啦。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| #include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include <thrust/universal_vector.h>
#include <cstdio>
#include "helper_cuda.h"
template <class Func>
__global__ void parallel_for(int n, Func func) {
for (int i = blockDim.x * blockIdx.x + threadIdx.x; i < n;
i += blockDim.x * gridDim.x) {
func(i);
}
}
int main() {
int n = 65536;
float a = 3.14f;
thrust::universal_vector<float> x(n);
thrust::universal_vector<float> y(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
x[i] = std::rand() * (1.f / RAND_MAX);
y[i] = std::rand() * (1.f / RAND_MAX);
}
parallel_for<<<n / 512, 128>>>(n, [a, x = x.data(), y = y.data()] __device__(
int i) { x[i] = a * x[i] + y[i]; });
checkCudaErrors(cudaDeviceSynchronize());
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
printf("x[%d] = %f\n", i, x[i]);
}
return 0;
}
|
universal_vector 是基于统一内存分配的,因此无论在 GPU 还是 CPU 上,数据都可以直接访问。
使用分离的 device_vector 和 host_vector
device_vector 在 GPU 上分配内存,而 host_vector 则在 CPU 上分配内存。
可以通过 = 运算符在 device_vector 和 host_vector 之间拷贝数据,他会自动帮你调用 cudaMemcpy,非常智能。
比如这里的 x_dev = x_host 会将 x_host 中的数据复制到 GPU 上的 x_dev。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
| #include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include <thrust/device_vector.h>
#include <thrust/host_vector.h>
#include <cstdio>
#include "helper_cuda.h"
template <class Func>
__global__ void parallel_for(int n, Func func) {
for (int i = blockDim.x * blockIdx.x + threadIdx.x; i < n;
i += blockDim.x * gridDim.x) {
func(i);
}
}
int main() {
int n = 65536;
float a = 3.14f;
thrust::host_vector<float> x_host(n);
thrust::host_vector<float> y_host(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
x_host[i] = std::rand() * (1.f / RAND_MAX);
y_host[i] = std::rand() * (1.f / RAND_MAX);
}
thrust::device_vector<float> x_dev = x_host;
thrust::device_vector<float> y_dev = x_host;
parallel_for<<<n / 512, 128>>>(
n, [a, x_dev = x_dev.data(), y_dev = y_dev.data()] __device__(int i) {
x_dev[i] = a * x_dev[i] + y_dev[i];
});
x_host = x_dev;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
printf("x[%d] = %f\n", i, x_host[i]);
}
return 0;
}
|
使用 Thrust 模板函数:thrust::generate
Thrust 提供了与 C++ 标准库类似的模板函数,例如 thrust::generate(b, e, f),它的作用与 std::generate 相似,能够批量生成数据并填充到区间 [b, e) 中。第三个参数是一个函数,这里我们使用了一个 lambda 表达式。
前两个迭代器参数分别是 device_vector 或 host_vector 的开始和结束迭代器,可以通过成员函数 begin() 和 end() 获取。第三个参数可以是任意函数,这里用了 lambda 表达式。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
| #include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include <thrust/device_vector.h>
#include <thrust/generate.h>
#include <thrust/host_vector.h>
#include <cstdio>
#include "helper_cuda.h"
template <class Func>
__global__ void parallel_for(int n, Func func) {
for (int i = blockDim.x * blockIdx.x + threadIdx.x; i < n;
i += blockDim.x * gridDim.x) {
func(i);
}
}
int main() {
int n = 65536;
float a = 3.14f;
thrust::host_vector<float> x_host(n);
thrust::host_vector<float> y_host(n);
auto float_rand = [] { return std::rand() * (1.f / RAND_MAX); };
thrust::generate(x_host.begin(), x_host.end(), float_rand);
thrust::generate(y_host.begin(), y_host.end(), float_rand);
thrust::device_vector<float> x_dev = x_host;
thrust::device_vector<float> y_dev = x_host;
parallel_for<<<n / 512, 128>>>(
n, [a, x_dev = x_dev.data(), y_dev = y_dev.data()] __device__(int i) {
x_dev[i] = a * x_dev[i] + y_dev[i];
});
x_host = x_dev;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
printf("x[%d] = %f\n", i, x_host[i]);
}
return 0;
}
|
使用 Thrust 模板函数:thrust::for_each
同理,thrust::for_each(b, e, f) 对标 C++ 的 std::for_each,用于对区间 [b, e) 中的每个元素 x 调用函数 f(x)。其中,x 实际上是一个引用。如果使用常量迭代器,则是常引用,可以通过 cbegin() 和 cend() 获取常值迭代器。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
| #include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include <thrust/device_vector.h>
#include <thrust/for_each.h>
#include <thrust/generate.h>
#include <thrust/host_vector.h>
#include <cstdio>
#include "helper_cuda.h"
template <class Func>
__global__ void parallel_for(int n, Func func) {
for (int i = blockDim.x * blockIdx.x + threadIdx.x; i < n;
i += blockDim.x * gridDim.x) {
func(i);
}
}
int main() {
int n = 65536;
float a = 3.14f;
thrust::host_vector<float> x_host(n);
thrust::host_vector<float> y_host(n);
thrust::for_each(x_host.begin(), x_host.end(),
[](float &x) { x = std::rand() * (1.f / RAND_MAX); });
thrust::for_each(y_host.begin(), y_host.end(),
[](float &y) { y = std::rand() * (1.f / RAND_MAX); });
thrust::device_vector<float> x_dev = x_host;
thrust::device_vector<float> y_dev = x_host;
thrust::for_each(x_dev.begin(), x_dev.end(),
[] __device__(float &x) { x += 100.f; });
thrust::for_each(x_dev.cbegin(), x_dev.cend(),
[] __device__(float const &x) { printf("%f\n", x); });
parallel_for<<<n / 512, 128>>>(
n, [a, x_dev = x_dev.data(), y_dev = y_dev.data()] __device__(int i) {
x_dev[i] = a * x_dev[i] + y_dev[i];
});
x_host = x_dev;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
printf("x[%d] = %f\n", i, x_host[i]);
}
return 0;
}
|
- 当然还有 thrust::reduce,thrust::sort,thrust::find_if,thrust::count_if,thrust::reverse,thrust::inclusive_scan 等。
Thrust 模板函数的特点:自动决定 CPU 或 GPU 执行
Thrust 的 for_each 可以作用于 device_vector 也可以作用于 host_vector。当作用于 host_vector 时,函数会在 CPU 上执行,而作用于 device_vector 时,则会在 GPU 上执行。
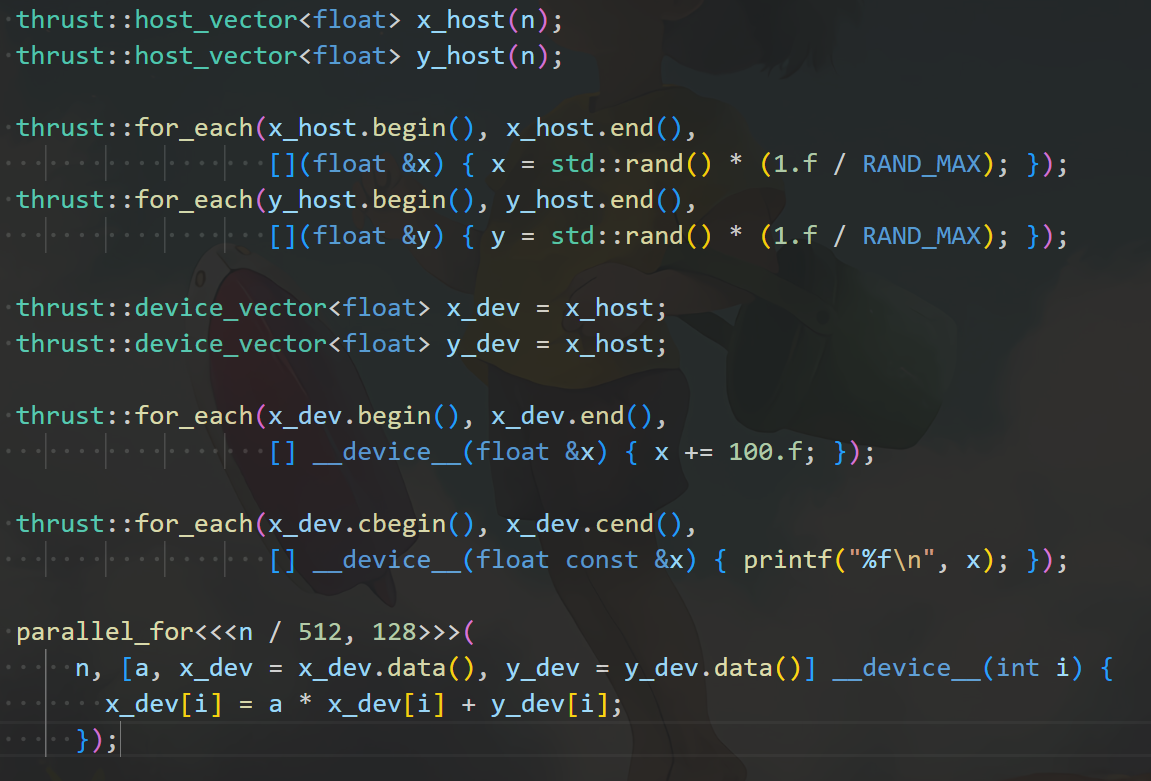
例如,针对 x_host 使用 for_each 时,lambda 表达式不需要修饰,而针对 x_dev 使用时,lambda 表达式需要加上 __device__ 修饰符。
使用 counting_iterator 实现整数区间循环
Thrust 中的迭代器区间操作(如 thrust::for_each、thrust::transform、thrust::reduce 等)通常基于迭代器区间。counting_iterator 是一种特殊的迭代器,能够生成递增的整数序列,适合用于这种情况。
这是 Thrust 提供的一种特殊的迭代器,当需要在 Thrust 算法中使用一个递增整数序列时,counting_iterator 就可以作为迭代器传递
counting_iterator 实际上是一个生成器,它的作用是 生成一个递增的数值序列
用 thrust::make_counting_iterator(num) 构建一个计数迭代器,他作为区间表示的就是整数的区间。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| #include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include <thrust/device_vector.h>
#include <thrust/for_each.h>
#include <thrust/generate.h>
#include <thrust/host_vector.h>
#include <cstdio>
int main() {
thrust::for_each(thrust::make_counting_iterator(0),
thrust::make_counting_iterator(10),
[] __device__(int i) { printf("%d\n", i); });
return 0;
}
|
使用 zip_iterator 合并多个迭代器
zip_iterator 可以看作是一个复合迭代器,它将多个容器(或迭代器)作为输入,生成一个新的迭代器,这个新的迭代器能够同时访问所有输入容器中对应位置的元素。在每次迭代时,zip_iterator 会返回多个容器中相应位置的元素。
可以通过 thrust::make_zip_iterator(a, b) 将多个迭代器合并,就像 Python 中的 zip 函数一样。
在使用时,可以通过 auto const &tup 来捕获每次迭代返回的元组,并使用 thrust::get<index>(tup) 获取其中第 index 个元素。之所以这么处理,是因为 Thrust 需要兼容一些使用较老标准(如 C++03)的程序,尽管现在可以更简洁地使用 C++11 的 std::tuple 和 C++17 的结构绑定语法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
| #include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include <thrust/device_vector.h>
#include <thrust/for_each.h>
#include <thrust/generate.h>
#include <thrust/host_vector.h>
#include <cstdio>
#include "helper_cuda.h"
template <class Func>
__global__ void parallel_for(int n, Func func) {
for (int i = blockDim.x * blockIdx.x + threadIdx.x; i < n;
i += blockDim.x * gridDim.x) {
func(i);
}
}
int main() {
int n = 65536;
float a = 3.14f;
thrust::host_vector<float> x_host(n);
thrust::host_vector<float> y_host(n);
auto float_rand = [] { return std::rand() * (1.f / RAND_MAX); };
thrust::generate(x_host.begin(), x_host.end(), float_rand);
thrust::generate(y_host.begin(), y_host.end(), float_rand);
thrust::device_vector<float> x_dev = x_host;
thrust::device_vector<float> y_dev = x_host;
thrust::for_each(thrust::make_zip_iterator(x_dev.begin(), y_dev.cbegin()),
thrust::make_zip_iterator(x_dev.end(), y_dev.cend()),
[a] __device__(auto const &tup) {
auto &x = thrust::get<0>(tup);
auto const &y = thrust::get<1>(tup);
x = a * x + y;
});
x_host = x_dev;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
printf("x[%d] = %f\n", i, x_host[i]);
}
return 0;
}
|
这样,我们能够通过 zip_iterator 同时操作多个容器。








